Corporate Highlights | Stay Connected with Renon
Stay up to date with Renon Power’s latest developments. Watch corporate videos, exhibition highlights, and global event coverage to witness our continuous growth and innovations in the energy storage industry.
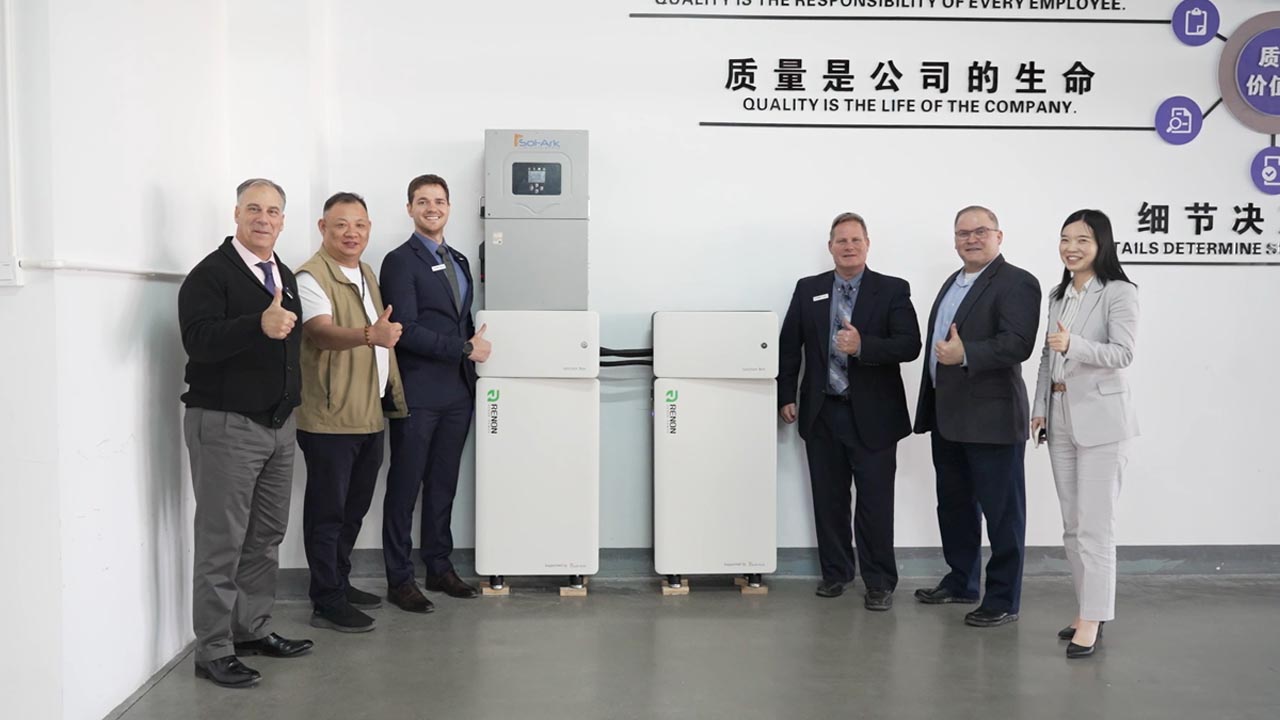

We were honored to host Sol-Ark at Renon! Together, we explored cutting-edge energy storage solutions and shared ideas to drive a sustainable future.
Strong partnerships lead to brighter tomorrows.
Watch the highlights from this inspiring visit!

Welcome to our channel! In today’s video, we delve into a pressing concern for many homeowners: the rising costs of electricity and the uncertainty of power outages. If you’ve ever felt the sting of a high electric bill or the anxiety of potential blackouts, this video is for you!

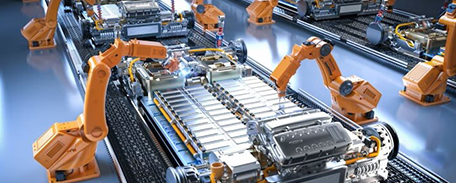
This video showcases Renonpower s digitalized intelligent manufacturing.
Renonpower builds an automated, interconnected and self-optimizing smart factory. Automated warehousing and logistics streamline material flows. Modularized and reconfigurable production lines enable flexible manufacturing. Real-time data monitoring and analytics optimize the entire value chain via MES. Quality is assured through coordinated inspection from raw materials to finished goods.

This video presents Renonpower s comprehensive quality management system in detail. Renonpower implements stringent quality control across its operations from R&D and manufacturing to customer service. Certified to international standards, Renonpower ensures the high performance and reliability of its products. Continuous optimization of the quality system through digitalization and data analytics helps us improve quality and management excellence to deliver customer satisfaction.